Procurement savings encompass more than just securing a lower price.
The Impact of Procurement on Profitability
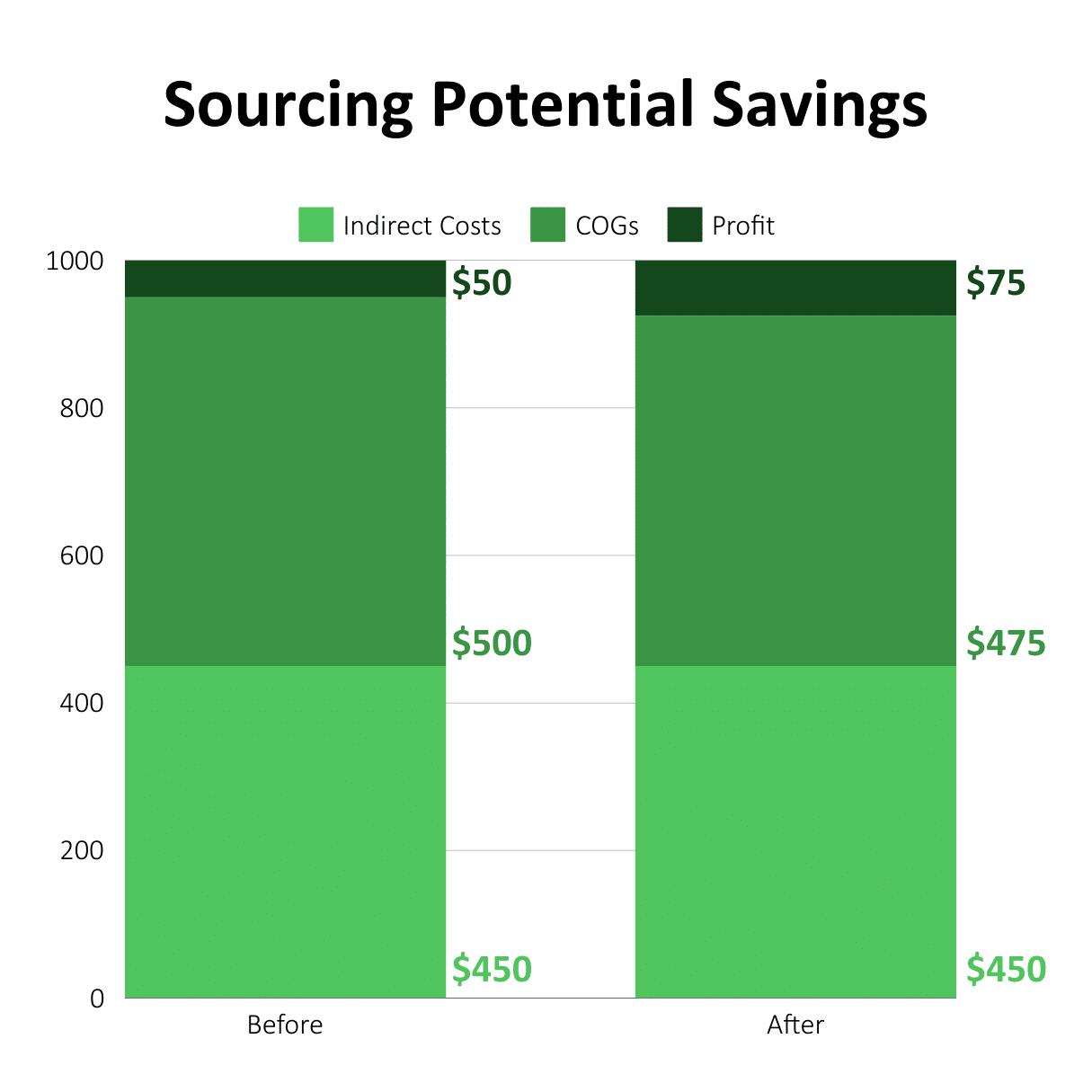
In various industries, the cost of purchasing goods and services accounts for 40% to 70% of total revenue. Thus, reducing the cost of goods sold (COGS) can have a significantly larger impact on profit than either increasing sales or cutting overhead expenses. Consider this example: a 5% reduction in COGS can result in a 50% increase in profit. To achieve a similar increase through sales, revenues would need to be boosted by 50%.
The Focus on Strategic Procurement
Businesses, regardless of size, aim to enhance their profits. However, in the procurement realm, the focus often narrows to negotiating lower prices with vendors. By shifting towards a strategic perspective of the source-to-pay business processes, companies could realize greater benefits without affecting their vendors’ profit margins.
Achieving Strategic Benefits
Achieving these benefits requires companies to create visibility and a comprehensive understanding of their key vendors, establish appropriate processes and metrics for the procurement department that promote a holistic approach to purchasing, and implement processes and metrics that sustain these savings through timely feedback and discussions with key vendors.
The goal is to integrate strategic sourcing and supply management with supportive technologies, efficient procurement infrastructure, operations, and metrics.
For large companies, this strategy can lead to savings in the millions of dollars; for smaller companies, the savings potential is also significant.
Steps to Achieve Procurement Benefits
Step 1: Understand Spending and Vendor Participation
Step 1 involves understanding your company’s spending and vendor participation. This includes knowing how much you spend with key vendors, what products and services are purchased, reviewing existing contracts to understand terms and conditions, understanding your market and the market for essential COGS items, establishing relationships with major vendors open to negotiation, and identifying opportunities for savings.
The aim of Step 1 is to comprehensively understand spending patterns and procurement practices. Once the data is gathered, the company can identify opportunities to reduce costs. For instance, a small classic auto import company achieved cost reductions by consolidating its suppliers and negotiating prices based on the supplier’s full annual capacity. Similarly, a small contractor enhanced their contractors’ productivity by pre-packaging materials needed for daily tasks, reducing morning preparation time.
Identifying quantifiable savings and highlighting these opportunities on the “Opportunity Wall” concludes this step.
Step 2: Modify Source-to-Pay Processes
Step 2 focuses on identifying business requirements, determining key suppliers for the program, evaluating your market participation, establishing clear supplier management expectations, developing a supplier report card, and incorporating your actions into this evaluation.
This step involves modifying the source-to-pay processes and infrastructure. It’s crucial to understand the true cost of purchasing, including the item’s price and the additional costs associated with sourcing, purchasing, and paying for it. Factors affecting overall purchasing costs include the volume of spending, current contractual agreements, product or service complexity, the supplier’s competitive position, and product quality, among others. Streamlining these processes can lead to significant cost reductions.
Step 3: Improve Procurement Organization and Culture
Step 3 is about improving the procurement organization’s skills, creating compliance mechanisms, streamlining business processes, and realigning the company culture.
Viewing procurement improvement as a one-off event leads to the loss of savings over time. Continuous improvement and change creation processes are essential to maintaining benefits. Savings can evaporate due to changes in product lines, technologies, management focus, the vendor pool, and market conditions.
Key Areas of Focus for Effective Procurement
To create an effective procurement organization, the management team must focus on five key areas:
- Strategy: Develop a vision and strategy for procurement, differentiating between strategic and commodity products and services.
- Process: Measure and simplify processes, considering the specific needs of different commodities.
- Technology: Integrate technology with business processes for a comprehensive solution.
- Organization Structure: Design an appropriate organizational structure and measurement system to capture savings opportunities efficiently.
- People: Ensure management support, provide holistic training, and establish metrics that drive desired changes, moving beyond mere price reduction to include total acquisition cost.
This process is applicable to companies of all sizes and across both manufacturing and service industries. Planning, acting, measuring, and enhancing your bottom line through these steps can unlock substantial savings.